CAT BREED KEY TRAITS:
B - Bobtail
C - Curled fur
CE - Curled ears
F - Flat faced
FE - Folded ears
H - Hairless
O - Oriental
P - Point only
PD - Polydactyl
T - Tabby only
✦
☁ - Hypoallergenic
THE CAT BREED MASTERLIST is created with the express purpose of sharing details on every cat breed recorded.
ᗢ
This site includes extinct, new, experimental, unofficial or lesser known breeds not recognised by official cat associations such as The International Cat Association (TICA), Cat Fanciers Association (CFA) and Fédération Internationale Féline (FIFe).
ᗢ
Due to the popularity of some breeds over others, many lesser known breeds will have less information than others.
ᗢ
The site will be updated and each breed categorised based on common traits every time a new breed is recorded or found by the creator.
this site is best experienced viewing through desktop rather than mobile
ᗢ
This site will NEVER endorse or use AI for any pictures or writing. The owner prefers to use real pictures of real cats unless stated otherwise.
If you happen to realise any picture is AI generated, please do not hesitate to contact the owner to get it fixed
ᗢ
Cat patterns such as calico's, tortoiseshells, tuxedo, bicolour and tabbies are NOT cat breeds and will not be considered as such on this site.ᗢthis website is still in progress and will continue to update, if you would like to see future update ideas, check out the about.
if you would like to donate, feel free to donate to my paypal
CAT COAT COLOURS
Cats can come in so many colours and patterns, and whilst some breeds are colour and pattern specific, almost any breed can have any colour and pattern.
Both moggies and purebred cats can come in such a variety of colours and patterns as well as fur lengths and body types.ᗢThere are four main colours and two series.
Black based (aka Eumalenin) consists of Black, Chocolate and Cinnamon colours.
Red based (aka Phaomelanin) and consists of Red/Orange colours. All red/orange cats are tabby, there is no true solid red cat.

ID: A solid shorthair black cat with green eyes perched on a gate outside, it is day time and there is a roof and tree in the background

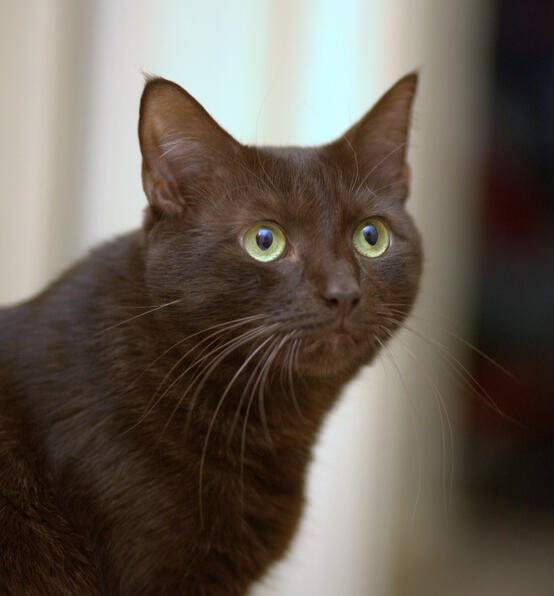
ID: A solid chocolate shorthair cat with pale green eyes in front of a blurry background

ID: A solid cinnamon oriental shorthair cat with green eyes sitting in front of a green background

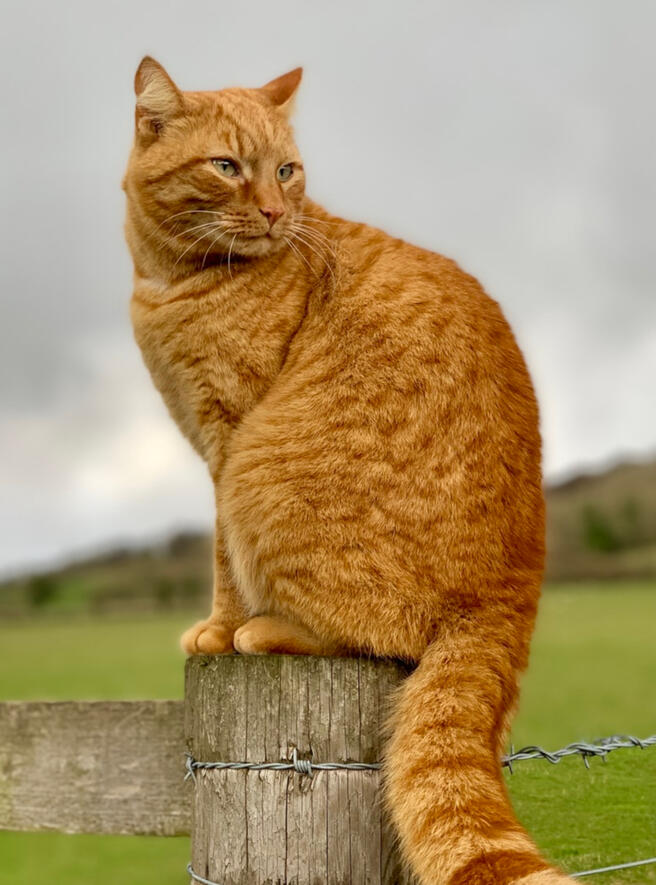
ID: A ginger tabby cat with spots sitting on a fence post outside, behind him is a blurred paddock with a hill and grey sky
After these four colours, we then move onto dilute cat colours. Dilute cats are usually lighter than their original counterparts, they are recessive traits to the dominant colours.
Black fur becomes blue/grey, Chocolate becomes Lilac/Lavender, Cinnamon becomes Fawn or a lighter lilac and Red becomes cream.

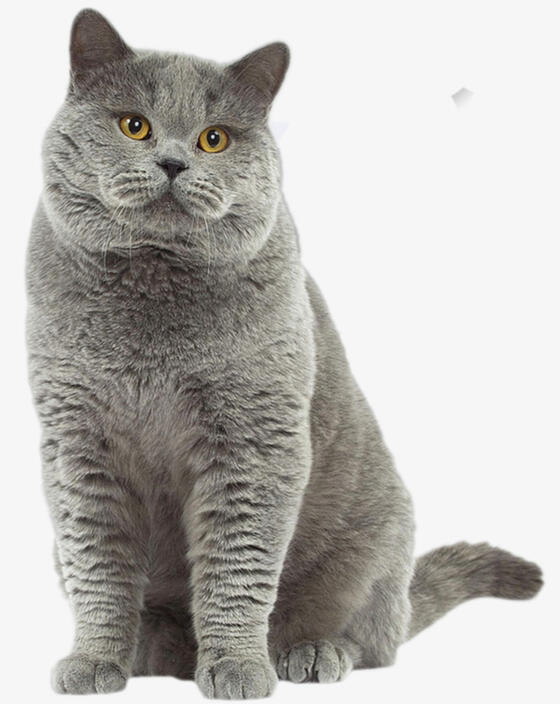
ID: A grey british shorthair cat sitting in front of a white background facing the camera

ID: A lilac british shorthair cat hunched over outside facing to the front left, the background is blurry

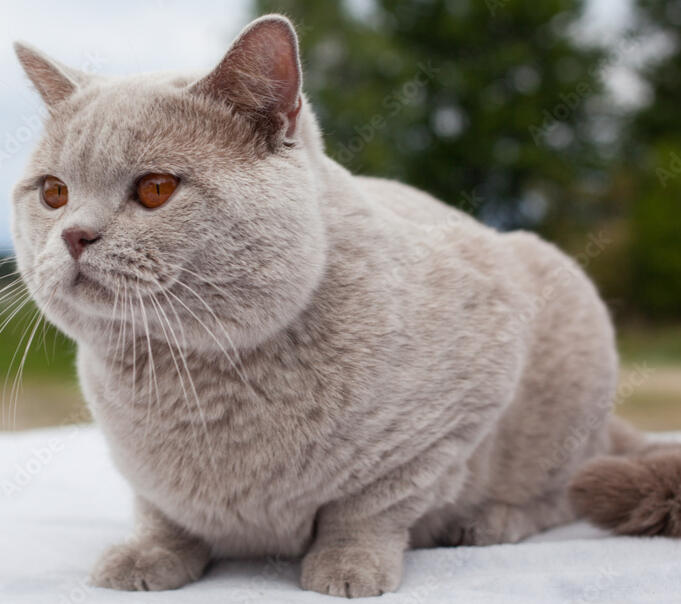
ID: A solid fawn coloured british shorthair cat with amber eyes, the cat is sitting with its head poked between two white wooden fence posts, its paws are sticking out underneath it.

ID: A cream striped tabby cat standing in front of a light creamy white background
Tabby cats are the most well known and iconic pattern for any cat, but they aren't actually breeds at all. Almost any cat can have tabby patterns, and every tabby can come in any colour.
When it comes to genetics, tabby cats are a dominant gene, its the reason you see more tabby cats, especially in the wild.
ᗢ
There are four main tabby patterns
Classic tabby, Mackerel Tabby, Spotted tabby and Ticked tabby.

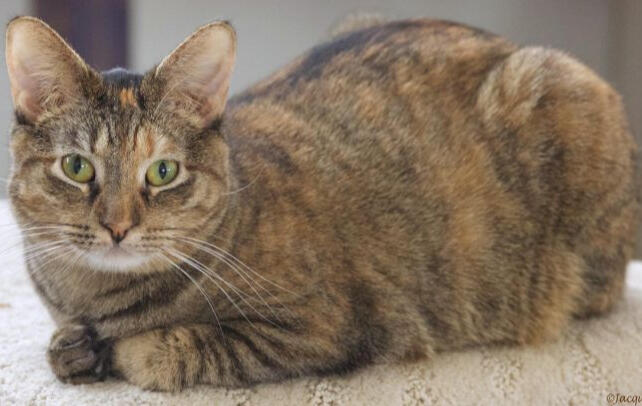
ID: A red classic American shorthair cat sitting down. there are orange swirls and patches on its back with lighter red on the chest and between stripes. the background is green

ID: A black mackerel tabby cat standing towards the right in front of a white background, it is looking up with mouth open. it has black broken stripes along its side

ID: A black/silver spotted tabby is sitting in front of a cloudy blue/green background. It has black/dark grey spots all along its back with lighter silver fur.

ID: A chocolate ticked tabby standing and looking to the left in front of a white background. Its fur is a deep chocolate colour that gradients to a lighter choclate/brown with stripes on its legs, head and tail
When talking about tabby colour, the colour of the stripes are what you are referring to.
The three pictures below are all black tabby cats.
They all look different however, the cat on the left being a black/silver classic tabby, the cat in the middle is a black/grey tabby, whilst the cat on the right being a black/brown classic tabby.
Genetically however, these three are both black classic tabbies.
The difference between a black/silver and black/grey tabby is prescence of the silver gene, which is only present in the black/silver tabby.
Whether a cat is silver can be identified by checking the base of the hairs.

ID: A black and silver classic tabby American shorthair, it is standing facing the left, but looking at the camera. The background is light grey

ID: A black and grey classic tabby shorthair cat standing facing the right, but it's head is turned towards the left. the background is a grey/brown mud/sand colour.

ID: A black and brown classic tabby Maine coon, it is standing facing the right and looking at the camera. The background is light grey/silver
There are other tabby types and even breed specific tabby types, such as Rosetted, Marbled, Agouti, Broken mackerel tabby and more!

ID: A shorthair bengal cat looking to the right, the bengal has black rosettes on its side with orange inside. its standing on wood with a green blurry background

ID: A shorthaired bengal cat facing the left and looking up, it has a black marble/clouded pattern with orange/brown fur in between. the background is a grey gradient.

ID: An abyssinian cat standing to the left but looking down to the right, it has a black ticked/agouti gradient pattern with cream chest and paws, the background is brown linel and a white blurry object behind it.

ID: A fluffy cat facing the right and looking at the camera, it has brown fur with broken black thin stripes all over its body. the background is blue gradient.
Tortoiseshell cats are another popular and well known pattern for cats. Like tabbies, calico and tortoiseshell cats aren't actually breed, instead they're a rather popular pattern that can be found in many moggies and breeds.
However, unlike tabbies, Calico and Tortie cats are almost 100% female, with only 0.03% being male.
All tortoiseshell's cats consist of two colours, one black based (Eumalenin) and one red based (Phaomelanin).
Non-dilute colours such as Black, Chocolate or Cinnamon can only pair with red,

ID: A picture of a black and red tortie cat sitting down forward facing and looking off to the right past the camera, sitting on dirt and grass in front of stone wall.

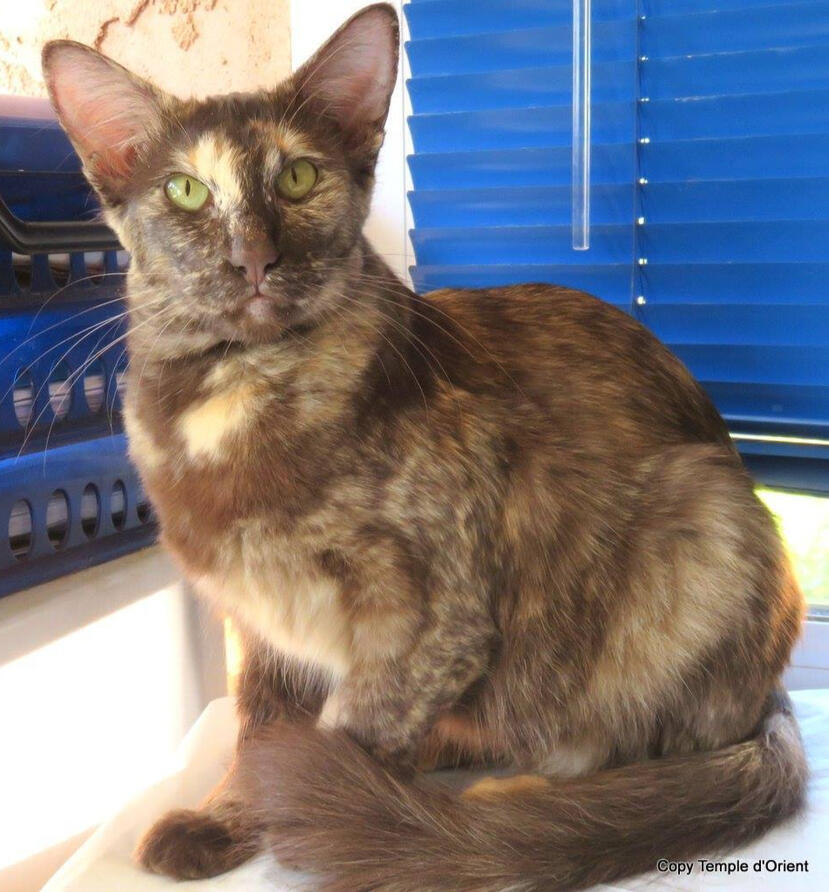
ID: A chocolate tortoiseshell oriental longhair sitting hunched over just a bit stairing at the camera, the background is light with blue blinds behind it.

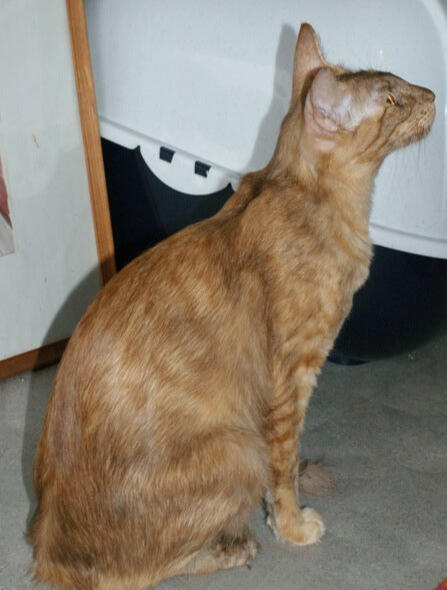
ID: A cinnamon tortie oriental cat sitting with its side to the camera looking to the right. It's head is tilted up looking at something above it. background is indoors with grey carpet, a wooden fram and a white wall.
whilst dilute colours Grey, Lilac and fawn are paired with cream.

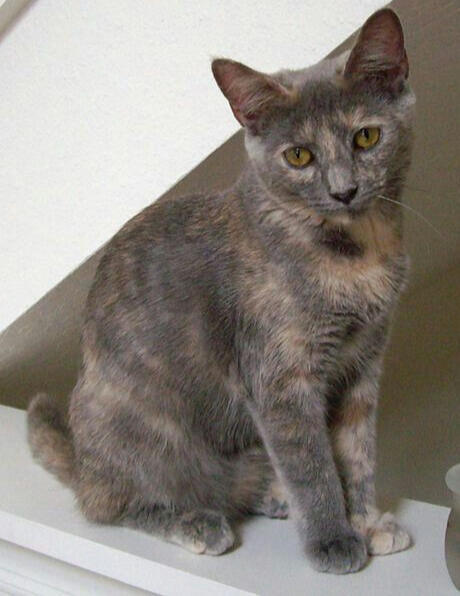
ID: a grey and cream tortie kitten sitting on a white ledge and looking down at the camera

ID: A lilac and cream tortie burmese cat, it's hunched over and looking at something off to the right out of camera view, background is different shades of biege.

ID: A fawn and cream oriental shorthair cat with faint mackerel tabby markings, the cat is hunched over facing the left and staring at the camera. the background is a cloud blue.
All red spotting of a tortoiseshell/calico cat has faint tabby stripes, as all red and cream cats are inherintly tabby. However, not all tortie/calico cats are actually tabbies.
It is when the black part (Eumalenin) of the fur has tabby patterns itself is when the tortoiseshell or calico are considered Tortie-Tabbies and Calico-Tabbies
Torbies or Calibies for short.
Patched is another term for torbies/Calibies
Just like any other Tabbies, Tortoiseshell, Calicos and Patched cats can come in any colour and tabby pattern!

ID: A shorthaired black and orange mackerel tabby-tortie loafing facing to the left and staring at the camera. background is blurred

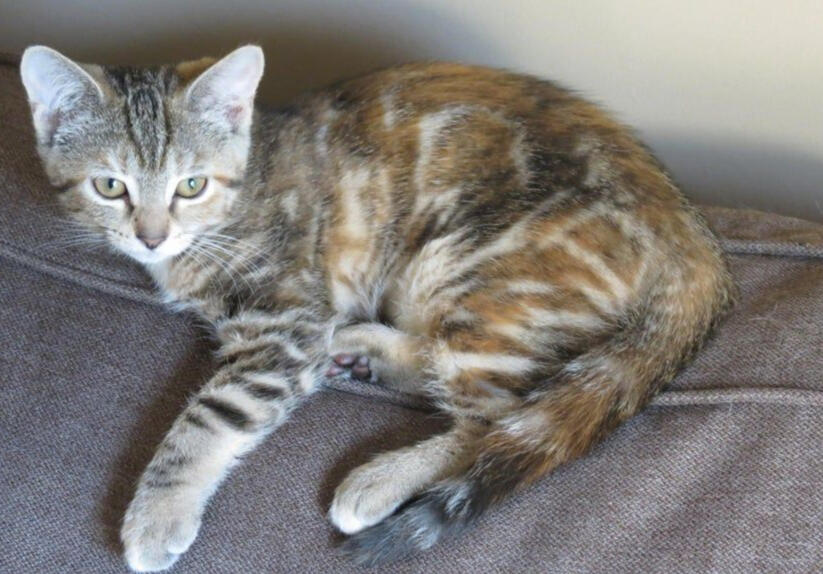
ID: A Black and orange classic tabby-tortie kitten laying on a grey-brown couch, it's facing left with one paw outstretched and looking at the camera.

ID: A dilute broken mackerel tabby-tortie lying on its site facing the left, it is looking over its shoulder to the right. laying on stones outisde in front of a bush.
When it comes to Calico cats, the difference between them and tortoiseshell cats are how much white spotting they have.
All tortoiseshell cats have a brindled pattern, but the more white spotting they have, the more distinct and bigger the black and red patches become.
However different cat sites and registaries may vary and it depends on the country and how they identify the difference between a calico or tortoiseshell.

ID: A black and red calico cat loafing on the corner of a white couch, it's facing left but looking at the camera. the background is various shades of brown.

ID: A black and orange spotted tabby-calico standing on a brown fence. it is facing the left and staring at the camera.

ID: A cinnamon and red longhaired calico with low white spotting standing to the left and looking at the camera. the background is black.

ID: a chocolate tabby-calico oriental longhair cat loafing on its right and staring at the camera, it is lying on a blanket and a blurry white cat sitting behind it.
ID for picture above: Title of the picture says "HOW WHITE SPOTTING AFFECTS TORTOISESHELL COLOUR DISTRIBUTION" underneath the title is four illustrated pictures of cats facing to the left, the lineart for each cat is the same, a shorthaired cat with a side profile of their body to show their patterns.
The far left cat is complettly black with red brindled splotches along its body, the second cat is almost exactly the same, but there is low level white spotting on the chin, neck, chest belly and paws.
The third cat is white with black and red patches that are more defined, the patches are on the head, all along the back and tail and a few patches on each leg.
The last cat is white with only a few red and black patches, only one on the head, three patches on the body and two black patches, one on the front and one on the back leg.
Under them is a blue arrow that starts from the left cat and goes all the way to the right.
under the arrow is text saying "AS THE AMOUNT OF WHITE SPOTTING INCREASES, THE TORTOISESHELL COLOUR BECOMES LESS BRINGLED AND FORMS DISTINCT PATCHES OF COLOUR.
THIS IS RELATED TO THE MIGRATION RATES OF PIGMENT CELLS ACROSS THE SURFACE OF THE EMBRYO"
/end ID
White spotting on cats is interesting, they can happen in almost any pattern, colour and breed. Consider the white spotting like paint, you have the main pattern, whether it be solid, tabby, tortoiseshell or point, and then you splash the cat with white over it.
Tuxedo, Bicolours, Harlequinn and Van cats are all different levels of white spotting.
White spotting usually starts from the paws and chest, covering up the belly and legs. Higher white spotting cats have the white spotting mask up the face and even back, reaching up to the tail and leaving only head/ear spots and tail tips.

ID: A grey tuxedo cat loafing facing the left with its eyes closed, on a tree stump, the background is blurred leaves.

ID: A black and white bicolour cat with white spotting on legs, chest and face. the cat is sitting to the left and looking off camera. sitting on a wooden table with a blurry grassy background with trees in the distance.

ID: A white cat with red harlequinn patches on its face, side, legs and tail, it is facing left and looking at the camera, it is standing on a tree.

ID: A white van cat with grey and cream patches on the lower back, tail and forehead. its back is to the camera but its head is looking over its shoulder at the camera. The background is medium blue
Dominant white cats or Epistatic white cats are different from cats with high white spotting and run on a different gene to black or red based colours.
Blue eyed white cats are well associated with deafness in cats, however it's only dominant white cats that are actually affected and have a high chance of being deaf.
White cats can also have amber, green or heterochromia eyes.
Some white kittens might be born with smudges of colour on their forehead's but they usually disappear by adulthood.
Genetically, White dominant cats may be any colour or pattern, but the white gene covers any other colours.

ID: a white shorthaired cat sitting and looking up at the camera, its eyes are hazel, the background is blurred brown.

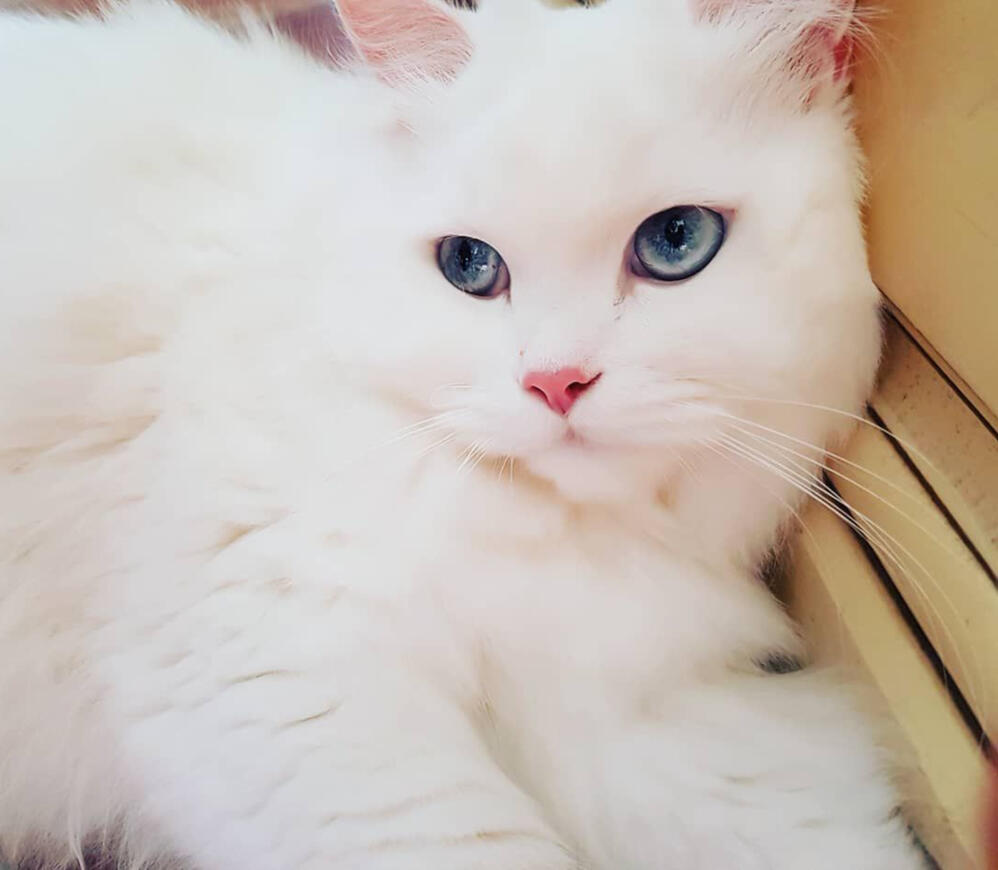
ID: a headshot of a white fluffy cat propped up against a brown wall, its eyes are blue

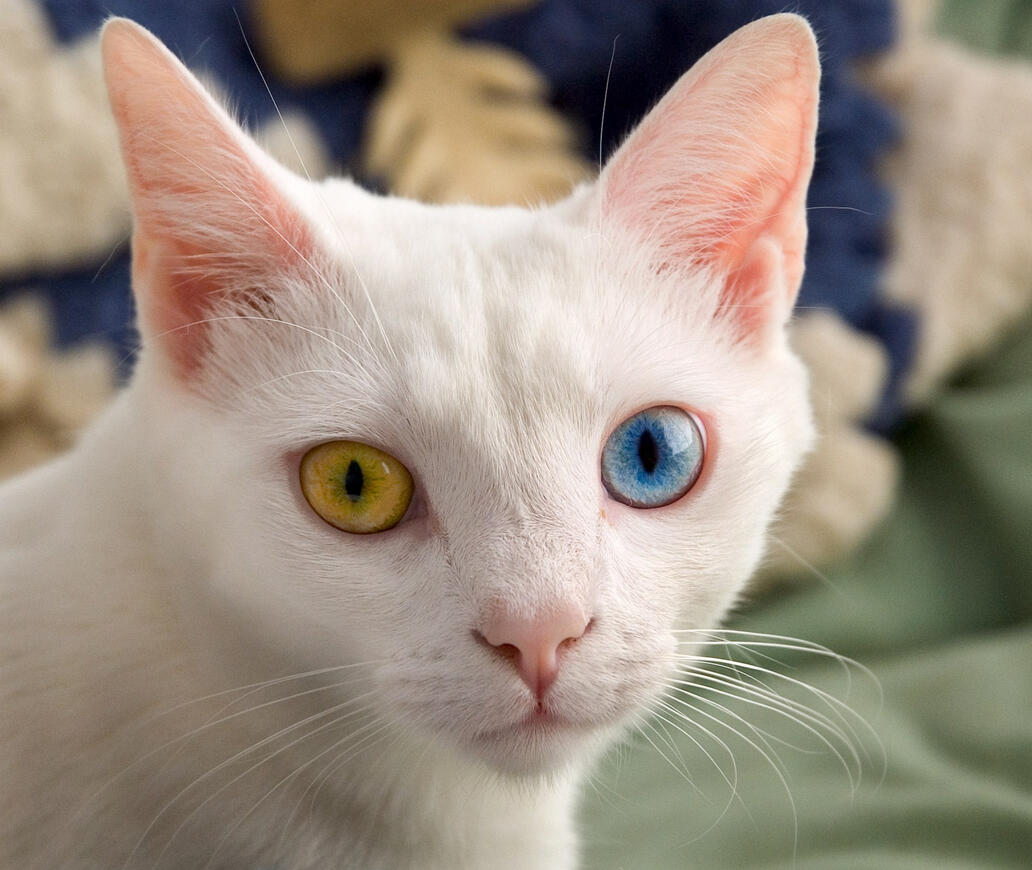
ID: a headshot of a white shorthaired cat stairing at the camera, the left eye is yellow and the right eye is blue. the background is a blurry green sheet with a blurry white and blue blanket.
Unlike Dominant white and white spotting, Albinism in cats is recessive. Dominant and white spotting cats still genetically have other patterns hidden or covered in white.
However, Albinism is a mutation that causes the cat to have a lack of any colour at all, this also includes pigment in the eyes.
Contrary to popular media and stereotypes, Albino cats eyes are more pink or blueish-pink eyes, which results in weaker eyes that are sensitive to light.
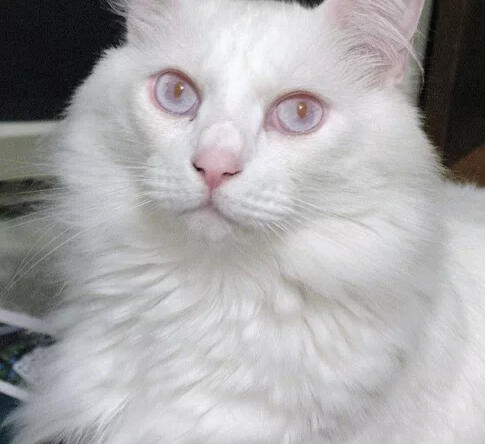

ID: A headshot of a fluffy albino cat , the cat is looking up at the camera, its eyes are a lilac/light blue almost white with red pupils. The background is a dark grey.
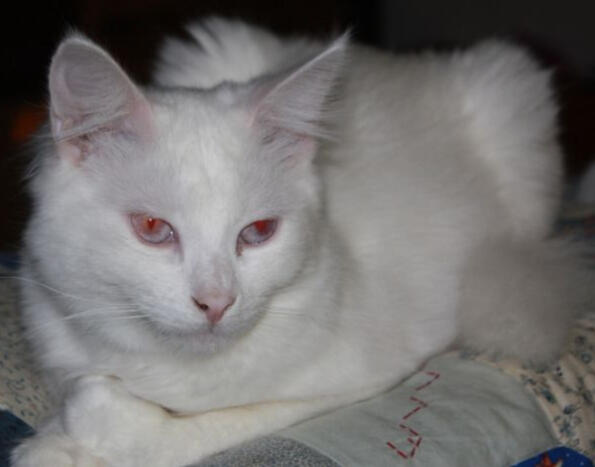

ID: An albino cat loafing on a white blanket, the cats eyes are hlaf closed. The eyes are a lilac/light blue and its pupils are red

ID: A fluffy albino cat staring up at the camera, the cat is loafing on grey carpet. it's eyes are a light blueish/purple
UNIQUE COLOURS AND PATTERNS
With a continuation on cat colours and patterns, this page is dedicated to more unique and breed specific patterns and colours.ᗢColourpoint cats are most well known for Siamese and Ragdoll cats, but can be present in many other breeds.
Colourpoint cats can have almost any pattern and colour, and have almost any level of white spotting.
Black point cats do exist, however they are labelled as Seal Point.
Red points are called Flame Point.
The point gene is recessive, meaning you need two parents that are point or point carriers in order to produce point kittens.
ᗢ
Blue eyes are a rare and unique eye colour for cats, and point cats are well known for having primarily ONLY blue eyes!
The point pattern is unique because it is technically heat sensitive albinism. The coolest parts of the cat showing the most colour.
Usually point cats who live in colder areas will have darker fur.
Point kittens all start off white and as they grow up their point pattern shows

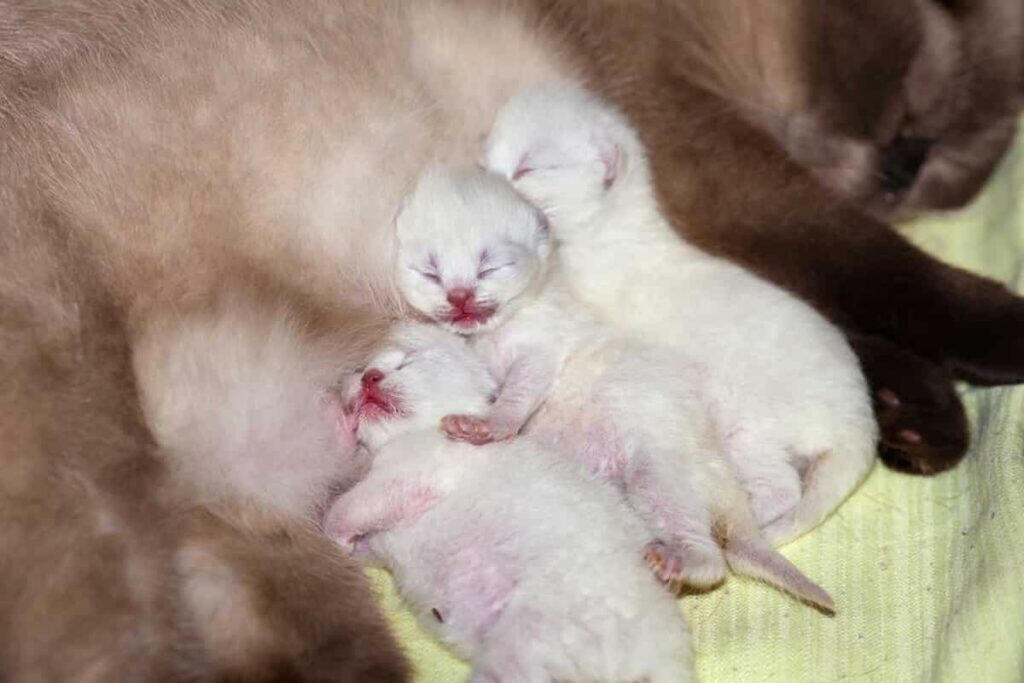
ID: A seal point mother cat lying down with three white newborn kittens snuggling up to her belly

ID: A mostly white and very young seal point kitten with a patch on their nose and ears.

ID: A seal point kitten that is slightly older with cream fur and a dark muzzle and ears
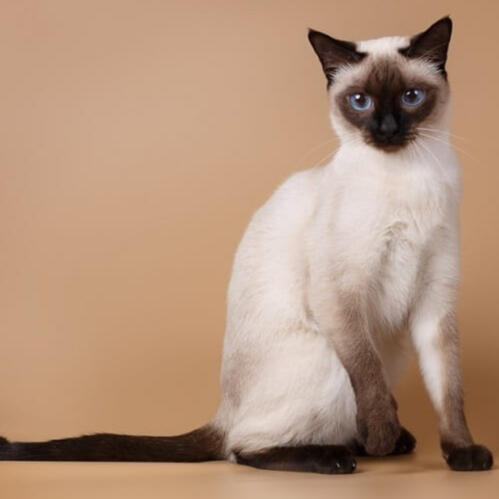

ID: A young adult seal point cat with most of its face, paws and tail have a seal point colouring. the rest of the body is a light cream.

ID: A seal point siamese cat with mostly dark pattern and dark brown fur on the back and head.
Mink, Sepia and Solid point cats are a darker gene of point cats that are most commonly seen in Burmese, Tonkinese, Ragdoll and Tibetan.
Unlike other point cats, Burmese cats do not have blue eyes, more commonly having yellow or orange eyes.
Ghost Tabbies are cats that are still genetically solid. All cats are technically tabbies, even the most solid looking cats. It is why sometimes in the sun you can see faint stripes and tabby markings on cats.
However, most of the time these markings fade as the cat grows older. However some adult cats can have more prominant ghost tabby markings.
Smoke Cats are different to silver cats in the cat that they are genetically solid. You can tell a cat is smoke by parting the fur and being able to see the base of the fur being silver that slowly transitions to the colour of the cat.
Any tabby like markings don't mean the cat is actually a tabby however. They are called ghost markings.
The Karpati pattern is rather new andd unique to cat genetics. Originally stated as a new breed, it seems to be the pattern of the transylvanian breed.
CAT GENETICS
Using the information from Cat Coat Colours, cat genetics can be quite simple if you know the basics. This page will not go into too much depth or detail, and will stick mainly to basic cat colours and patterns.This page is purely hypothetical, please do not leave your cat unfixed, please have your cats spayed. Cats that are not spayed can have well over 100 kittens and can be a huge danger to wildlife. Shelters are easily overrun with kittens and TNR costs a lot.ᗢLets start off with colours.
From dominant to recessive in black based (Eumalanin) cats it's:
Black - Chocolate - CinnamonDespite being different colours, chocolate and cinnamon are still black-based colours.
this means that Black is the dominant colour, Chocolate is recessive to black and Cinnamon is recessive to both black and Chocolate.
This just means for Chocolate and Cinnamon, both parents must be Chocolate/ Cinnamon or carriers of those colours in order for their kittens to be them.Dilute colours are more recessive than non-dilute:
Grey - Lilac - FawnThis means, if a black and grey cat have kittens, the majority of the kittens will be black. However, because the recessive gene is still there, the kittens have a chance of carrying the grey colours, and would have a more likely chance of having grey kittens themselves if their mates were grey.
Red/Cream colours (Phaomalenin) are co-dominant with Black based cats, which is the reason why we get calico/tortoiseshell cats.
When it comes to Phaomalenin in genetics male cats get only one colour from their mothers whilst female cats gets parents from both parents. That is how tortoiseshell's are made.
The majority of the time, ginger cats are male.If the mother is a black tortoiseshell and the dad is solid black, then the female kittens will be either all black or tortoiseshell, and the the male kittens will be either black or red.
It's only if the parents are both black based (Eumalanin) that the kittens can have either of their parents colour.
Alternatively, if the father is a red tabby, then the female kittens will either be tortoiseshell or red.
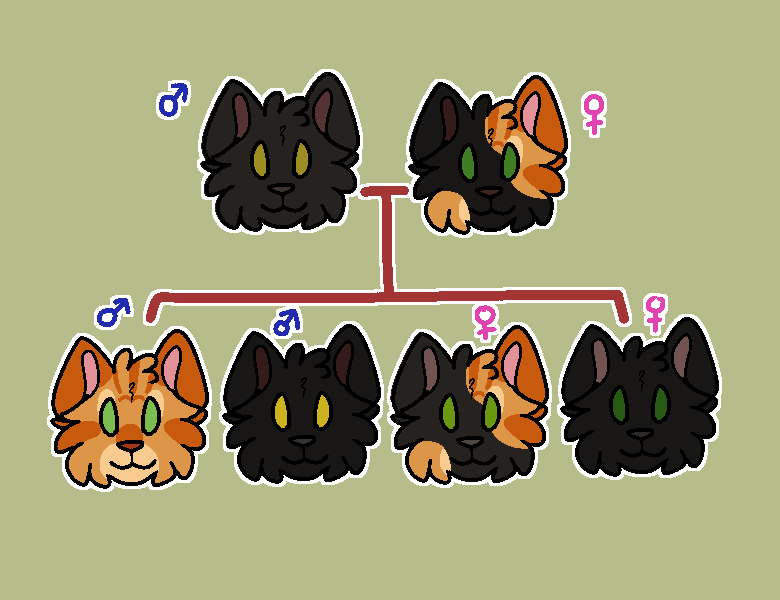
ID: Digital art of a family tree of cats. parent on left is black with blue male symbol above. parent on right is tortie with pink female symbol above. below are 4 kittens. ginger male, black male, black-tortie female, black female. each with gender symbol
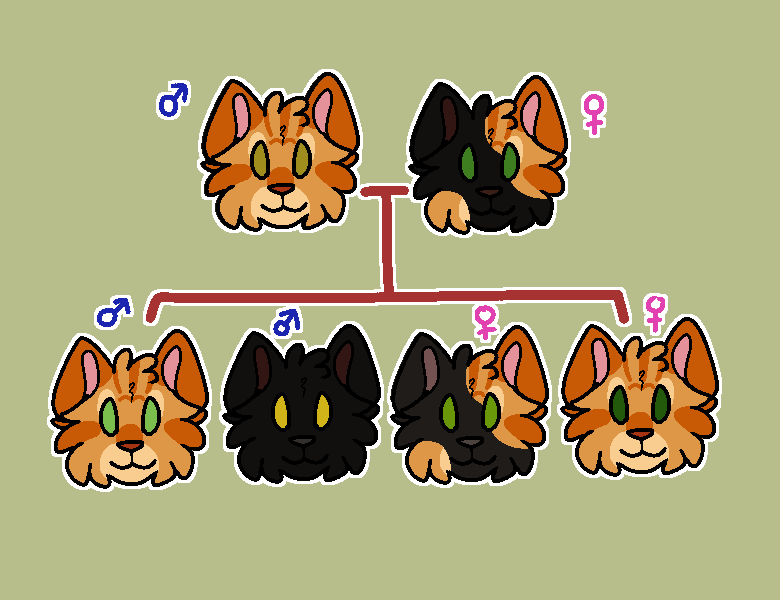
ID: Digital art of a family tree of cats. parent on left is red with blue male symbol above. parent on right is tortie with pink female symbol above. below are 4 kittens. ginger male, black male, black-tortie female, ginger female. each with gender symbol
The tabby pattern in genetics is also dominant, kittens with one tabby and one solid parent are more likely to inherit the tabby pattern.
Different tabby patterns are more dominant than others, but that doesn't equal popularity, as classic and mackerel tabbies are more popular than spotted or ticked.
from dominant to recessive:
Ticked - Spotted - Mackerel - Classic
White spotting is a dominant pattern, meaning that it doesnt matter what level of white spotting the parents have, the kittens can also have the same or roundabout.
However cats with only one or two spots on the belly/chest will not produce kittens with higher white spotting.
If one parent has no white spotting, and the other has more than half, the kittens will likely have less than half white spotting.
As mentioned before in the section about dominant white cats, pure white cats still carry other colour/pattern genes from their parents, for example they may be white, but both parents were tabby cats.
If a dominant white cat with the chocolate gene has kittens with a solid lilac cat, then the kittens will most likely be chocolate with white spotting. The kittens have a chance of being lilac or carrying the colour.
This works with any other pattern/colour combination
Fur length is also determined by genetics, short fur being dominant and long fur being recessive.
FUN FACT: when it comes to more unique fur types like hairless and curly fur, the hairless gene is recessive to normal fur types [both long and short] and curly fur is actually recessive to both normal and the hairless gene.From dominant to recessive in coat lengths
Short fur - long fur - no fur/hairless - curly furOther unique patterns and colours like Point, Smoke, Roan and lykoi fur are all recessive traits and follow the same rules as other recessive genes.
GENETICS EXAMPLE:
using the information from above, we can make theories one what kittens can look like from their parents. A hypothetical scenario for any OCs or characters one wanted to make for their projects, stories or art.
ᗢ
Sire: A black ticked tabby with medium white spotting and long fur.
Carries
-chocolate
-solid
Does NOT carry diluteDam: A solid lilac calico with tuxedo white spotting and short fur.
Carries
- long fur
All kittens can be shorthaired or longhaired.
They can be solid or any type of tabby, and can have any amount of white spotting.
Kittens will most likely not be dilute, however they will carry the dilute gene.Male kittens can be black, chocolate or red.Female kittens can be black, tortoiseshell, chocolate or chocolate tortoiseshell
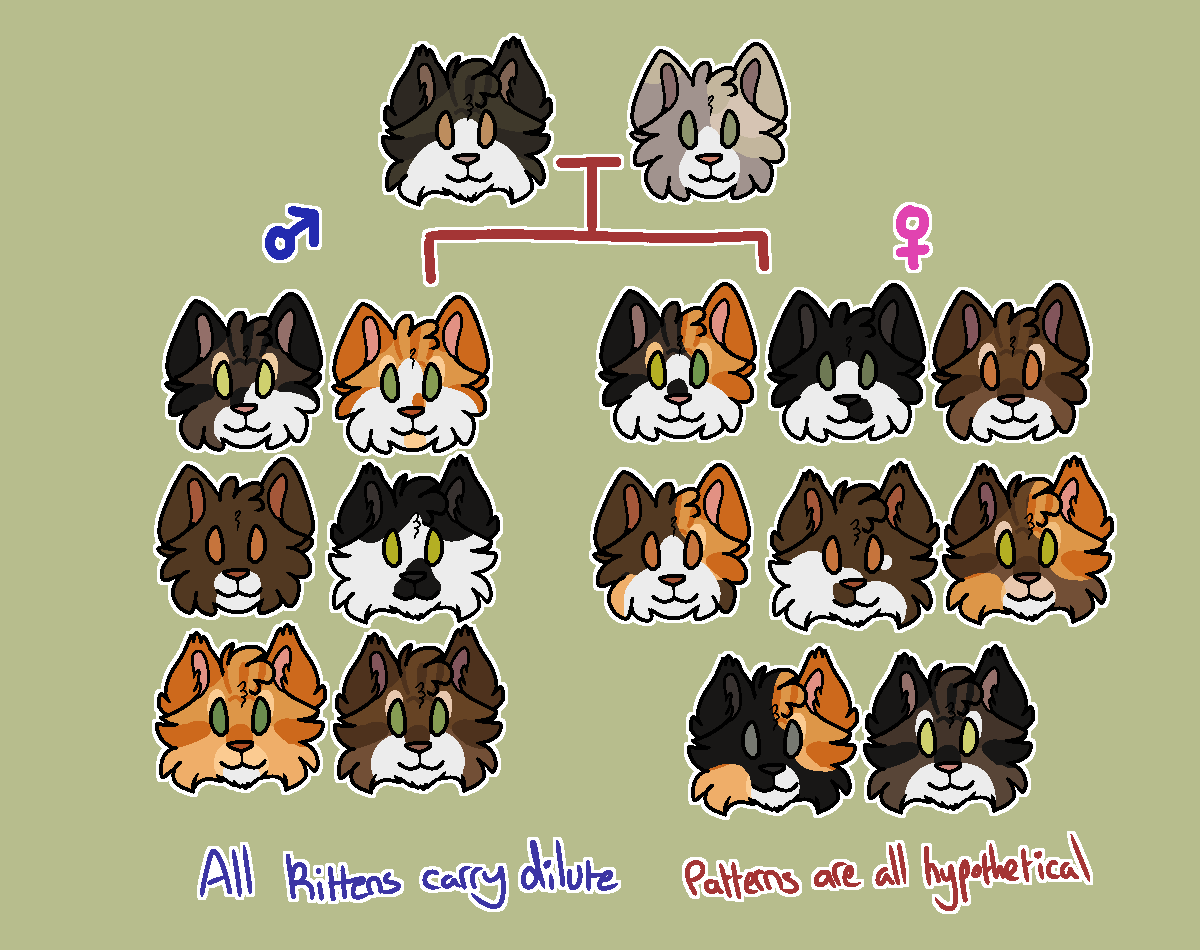
(ID for image above: A digital art picture of a family tree of cats, the first parent on the left is the Sire from above, A black longhaired tabby cat with white spotting, it's mate, the Dam is a shorthaired lilac calico with a white muzzle and chin.
Below them are two sections, on the left are six males and on the right are eight females, the gender symbols above each group. Each cat has different pattern combinations from the above genetics possibilities.
Male cats:
A black shorthaired tabby with white spotting on 1/4th of the face. lime green eyes.
A shorthaired ginger tabby with white covering bottom half of the face. Light green eyes.
A shorthaired chocolate solid cat with a white muzzle and chin. orange eyes.
A longhaired black and white cat with white covering most of the face except forehead, ears, nose and jowls. olive coloured eyes.
A longhaired ginger tabby with a white chin. Green eyes.
And a chocolate shorhaired tabby with white on the bottom half of the face. Light green eyes.
Female cats:
A shorthaired black tabby calico with white on the lower half of the face, and a small black nose spot. One green One olive eye.
A black and white shorthaired cat with white on lower half of face and a jowl spot. Grey/green eyes.
A chocolate shorthaired tabby cat with white muzzle and chin. Orange eyes.
A shorthaired chocolate calico cat with white mask and chin. Orange eyes.
A chocolate longhaired bicolour with half the face covered in white, a chocolate spot on the left jowl and right below the eye. Ginger eyes.
A chocolate longhaired calico-tabby with white spotting on the chin. Light green eyes.
A longhaired black calico cat with white spotting on the chin and the right jowl. Grey eyes.
A black longhaired tabby, with white over the muzzle and chin as well as above the eyes. Yellow eyes.
Under the family tree it says in Blue "All kittens carry dilute" and in red it says "Patterns are all hypothetical"
/ End ID)
Of course, this is just an example, and it doesn't cover every tabby or white spotting possibility.With it being just the basics of cat genetics, there is still more to do with smoke, point and other more Unique Patterns that are involved with cat genetics.If you would like to see more advanced genetics I recommend checking out Sparrows Garden.
CHIMERA CATS AND MUTATIONS
Chimera cats are an interesting phenomenon. Like any other chimera animal, a chimera cat is when two fertilised eggs fuse together in the womb.
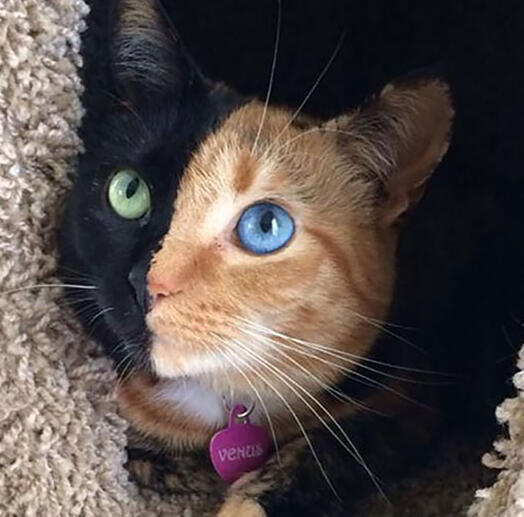
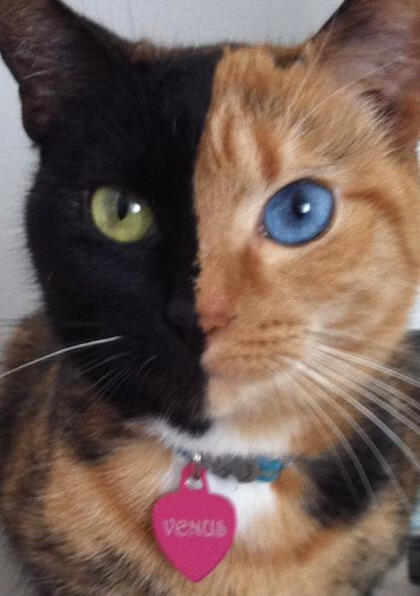
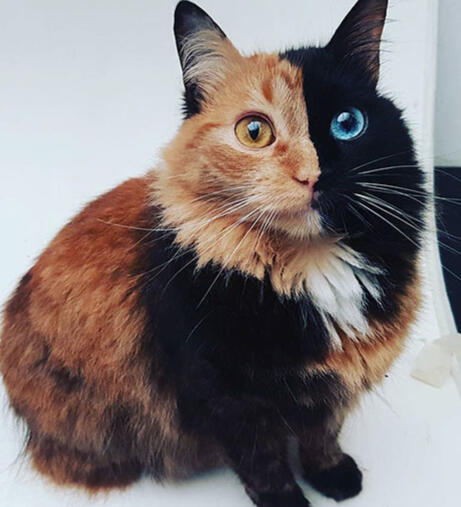
These iconic photos of cats below, with half their face as one colour, and the other side of the face another is a popular reference for Chimeraism in cats.
None of these cats are actually Chimera cats however, perfectly split faced torties are rare but that does not mean they are chimera cats.ᗢ
It can be hard to properly identify a chimera cat without proper DNA testing, however some chimera cats are easily identifyable due to their unique colours and patterns.

ID: A tortie cat looking up and to the left of the camera, her left side of the face is red, the right is black, her left eye is blue, the right is green. she has a pink heart collar with the name "venus". She is inside of a cat hidey hole.

ID: A tortie cat her left side of the face is red, the right is black, her left eye is blue, the right is green. she has a pink heart collar with the name "venus". Venus is staring at the camera

ID: A fluffy tortoiseshell cat staring up at the camera, the left side of her face is black with a blue eye, the right side of her face is orange with an amber eye, she is in front of a white background
(ID for image above: A white picture with multiple cats with different colours and patterns. Title at the top says "CHIMERA PATTERNS". Underneath the title is another text saying "A chimera is a result of two embryos merging early on. The cat is a mix of 2 different cell lines and can have unusual colour or pattern combinations."
On the left of the picture is a diagram surrounded by a blue border, it shows 2 colour dots, the left four are orange with "Embro 1" text on top, the left is grey with "Embryo 2" text.
Two red arrows point down together with text saying "Bump into each other and fuse together."
below that is a mix of grey and red dots with "Merged embryo" text on top.
one single red arrow pointing down says "continue to develop as a single individual" in text.
the arrow is pointing to a cat illustration, the cat is grey with strange orange patterns, text over the picture says "Chimera cat (2 cell lines in one body")
on the right of the box is a picture of 6 illustrated cats, each with text underneath.
first cat is beige tabby and black irregular spots, text says"Mix of solid + tabby cell-lines."
2nd cat is grey with black irregular spots, text says "Mix of dense + dilute colours"
3rd cat is cream with chocolate front body and point pattern text says. "Mix of pointed+ non-pointed"
4th cat is pure white with lines in different parts of the body symbolising longer fur patches, taxt says "Mix of longhair and shorthair patches (the patches may also be different colours)"
next line has the last two cats.
5th cat is beige tabby with black and orange irregular spots, text says "Mix of solid + tabby cell-lines where one embryo was tortoiseshell"
6th cat is grey with orange splotches, text says "mix of dense + dilute colours."
under that is another text that says "white spotting can occur on any of these patterns"
in the right bottom corner of the picture is an illustration of a cat head with a red cross over it. the cat head is half red and half black. text underneath says "A half-and-half face in normal tortie colours is not a sign of a chimera. It's a normal tortie variation!"
/ End ID)

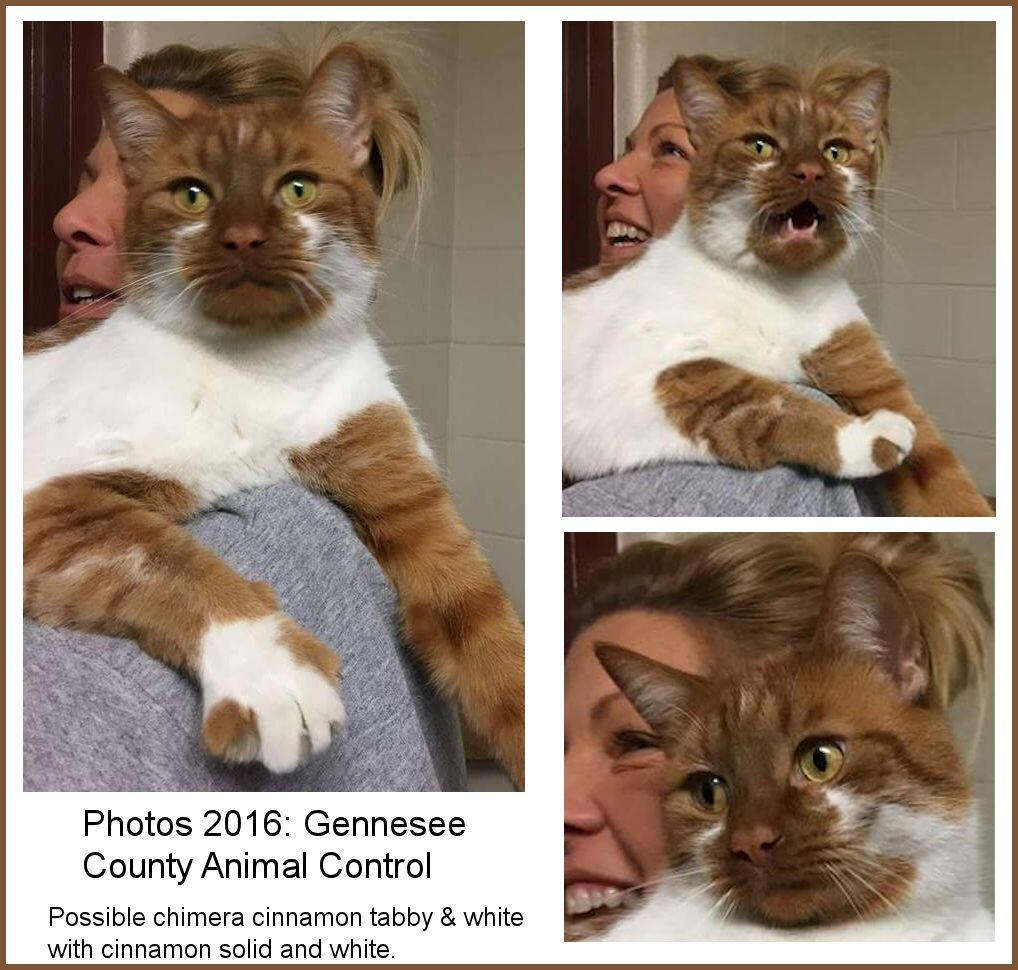
ID: three pictures of the same cat sitting on someones shoulder, it is white with cinnamon tabby patches, writing says "photos 2016: gennesee county animal control" underneath it says "possible chimera cinnamon & white with cinnamon solid and white"

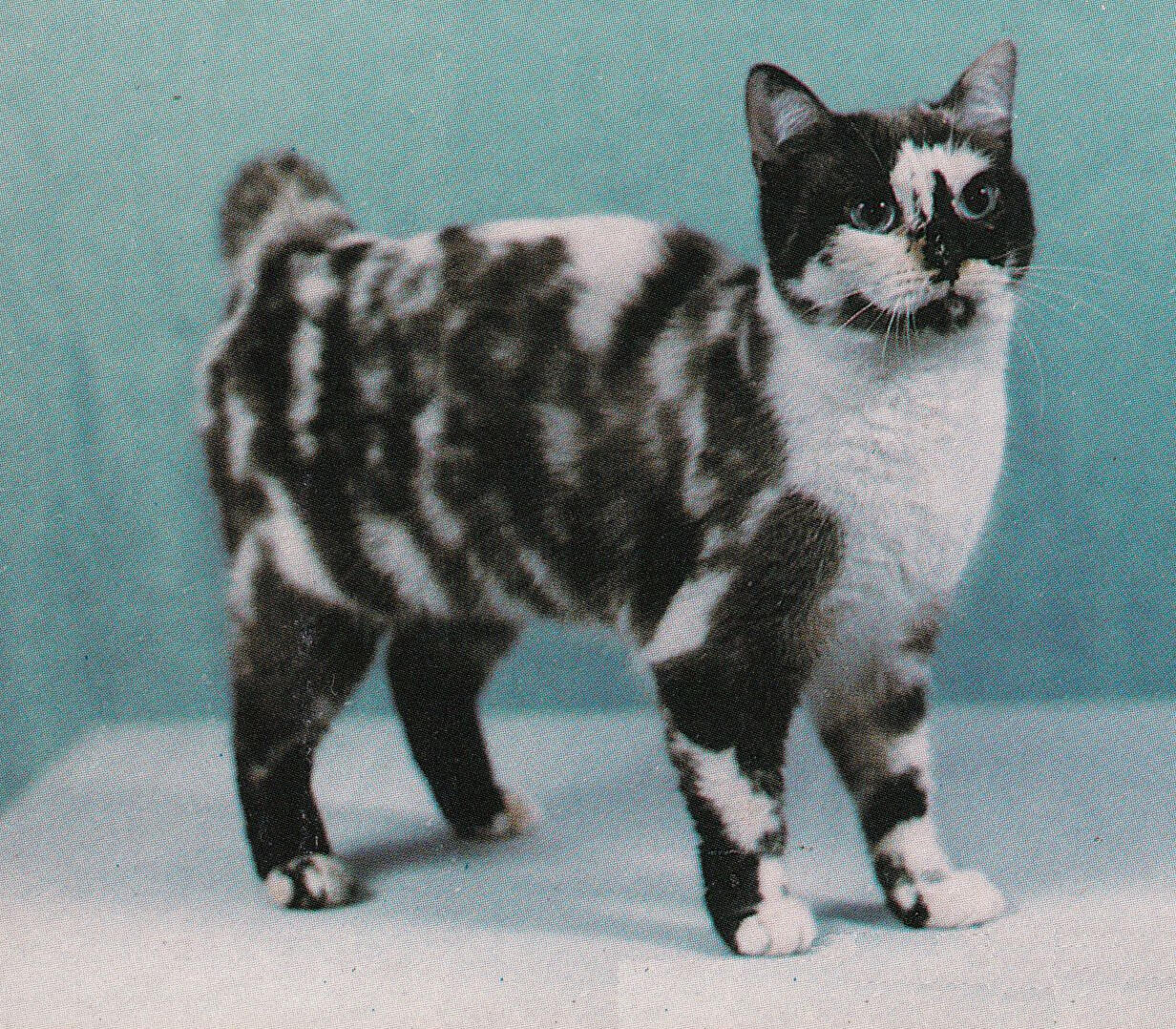
ID: A shorthaired bobtail cat is standing in front of a teal and white background facing the right. The cat is black and white, the white spotting is irregular and looks similar to a tortie cats pattern.

ID: A headshot of a shorthaired cat in front of a cream background, the cat is looking at the camera. half the face is black, there is a white stripe running up half the face with grey on the bottom half of the left face, and a bit of red above left eye.

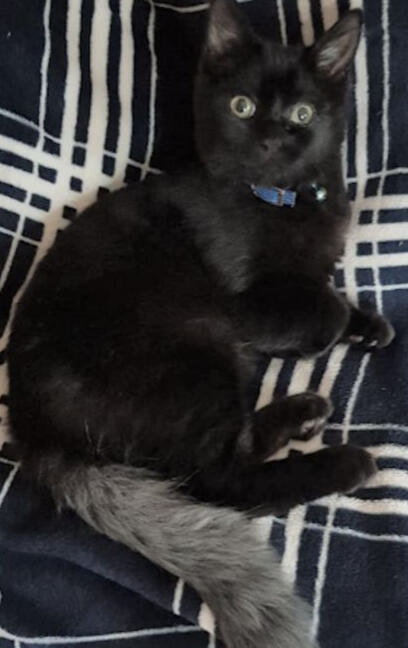
ID: A fluffy kitten lying on its side looking up at the camera, the background is black with white plaid stripes, the kitten is black with a grey tail and blue collar.
The Klinefelter Syndrome, also known as the XXY condition, or most commonly known as male calicos and tortoiseshell cats; are an interesting phenomenon.
When it comes to calico/tortoiseshell cats, the majority of them are female, actually, only 0.03% of calico/tortie cats are male. To put that in perspective, if you have around 3 thousand calico/tortie cats, only 1 of them would be male.
Male calico's are often infertile, but it is not impossible for them to have kittens.
The most common cause of calico/tortie tom cats is chimeraism, but not all calico tom cats are actually chimera cats.
ᗢ
When it comes to cat genetics, female cats have XX chromosomes and males only have XY chromosomes.
The X chromosome carries the coat colour, which is why females can have two colours, but males typically have one.
For a male to become a calico, they would have to have two X chromosomes, which is a genetic abnormality. This would result in XXY chromosomes.
ID: a six picture collage of the same cat in different angles, the cat is a tortie-tabby tom cat with short fur with high white spotting. one picture shows a close up of his testicles.
Text on the bottom right says "Tabby-tortie male "Odyssy". Photos by Emma Wiechmann North Queensland, Australia. He is obviously tabby-tortie-and-white and obviously male."
SOMATIC MUTATION
Vitiligo, like humans, can show up in cats as well. Most of the time, kittens are born without the white spotting but as they grow up the pattern grows and becomes more prominant.
ABOUT
I have been working on the Cat Breed Masterlist for years.
It started on a google document I would share around to everyone. However, it became unreadable as the breeds reached over 100.
In 2020 I moved to make a site on carrd.
However since then I have gotten better at using carrd, and I am now able to include unlimited assets and expand not just on cat breeds but also go into more details on cat genetics and colours.
Domestic cats have been a hyperfixation for many years, and my love for cat breeds made me want to make an accesable source for everyone to enjoy.
Many people have asked for this, many people still come up to me for advice, so making this site was something I really wanted to do.ᗢFUTURE UPDATE PLANS:
- Information pages about unique differences to more popular breeds.
( American vs European Oriental cats - Maine Coon vs NFC vs SFC - Sphynx vs Donskoy vs Peterbald)
- Every cat breed will link to a page dedicated to it, with breed characteristics and other information
- different types of mutations
-possibly more faux, extinct and lost breeds
ᗢDONATE TO SUPPORT ME AND MY PROJECT
the cat breed masterlist is a project made by someone who is not paid to do this, they work on this during their free time.If you have any questions or issues regarding the Cat Breed Masterlist, go here
QUESTIONS:
Q: Can I share this with other people/my friendsA: YES!! go ahead, I made this site as an open resource for everyone to use and share aroundᗢQ: can I make my own version with another animal?A: Absolutely, As long as it's not about domestic cats, feel free to make a carrd/site about any other animal and it's different colours/breeds.ᗢQ: You're missing [breed], could you add it?A: Yes! all breeds will be included, even if there is very little information. if they do not fit the main categories I may just add them to the Uncategorised list.ᗢQ: Can you help me with cat genetics for my ocs/cats?A: Go ahead! I am not always online or available, but if you would like to know something, shoot me an email, or if you would prefer to send me a message on social media, it's Dragofelid on all sites.
please note that whilst I love answering questions, I won't always have time to do so.